Introduction
Inductive sensors are widely used in automation to detect metal objects without contact. They are essential in systems where reliability and precision matter.
Two common installation types are flush (Built-in) and non-flush (Non Built-in) mounting. While both serve the same purpose, they differ in how they work, where they’re used, and how they’re installed.
This blog explains the key differences to help you choose the right type for your application.
Learn More: What is a Proximity Sensor?
Common Mounting Styles
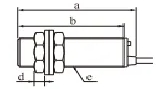
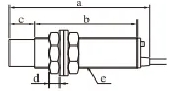
Flush mounting means the sensor is installed so its sensing face is level with the mounting surface. This design shields the sensor and focuses the magnetic field forward, making it ideal for applications where space is tight or where the sensor needs protection from damage.
Non-flush mounting means the sensor extends beyond the mounting surface. Without shielding, the electromagnetic field radiates from the front and sides, allowing for a longer sensing distance. However, the sensor is more exposed and requires a metal-free zone around it to avoid interference.
Understanding these differences is key to making the right choice for your machinery or automation setup.
Inductive Sensor Flush vs Non Flush: 8 Key Differences
| Difference | Flush Sensor | Non-Flush Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Magnetic field only emits from the front | Field emits from front and sides |
| Sensor Structure | Has shielding to block side field | No shielding; open design |
| Field Distribution | Narrow and focused field | Wide and extended field |
| Mounting Style | Can be embedded in metal | Requires metal-free space around |
| Sensing Distance | Shorter, more precise | Longer, covers a larger area |
| Environmental Suitability | Well protected from dust, impact, and moisture | More exposed, better in open, clean environments |
| False Trigger Risk | Low risk due to controlled field | Higher risk if near metal |
| Maintenance & Cost | More durable, lower maintenance needs | May require more frequent checks or replacement |
Operating Principle
Flush sensors focus the magnetic field forward. Non-flush sensors allow it to spread wider from the front and sides.
Learn More: The Ultimate Guide of Inductive Proximity Switch
Learn More: How Does a Proximity Sensor Work?
Sensor Structure
Flush types include a built-in shield to block side fields. Non-flush types are unshielded, allowing for a broader detection zone.
Electromagnetic Field
Flush sensors have a narrow, controlled field. Non-flush sensors cover a wider area but need more space.
Mounting Style
Flush sensors can be embedded in metal. Non-flush sensors require a metal-free space around them.
Sensing Distance
Flush sensors offer shorter but more precise sensing. Non-flush sensors can detect from farther away.
Environmental Suitability
Flush sensors are more protected and better in dusty or rugged environments. Non-flush sensors are better for clean, open setups.
False Trigger Risk
Flush types are less likely to be triggered by surrounding metal. Non-flush types need careful placement to avoid errors.
Maintenance and Cost
Flush sensors are more durable and need less maintenance. Non-flush sensors may wear faster if exposed to damage
Learn More: How to Test an Inductive Sensor: 6 Methods You Should Know
Conclusion
If your application involves tight spaces or exposure to metal, flush sensors are the safer bet. If you need a longer sensing range and have space, non-flush sensors are ideal.
Knowing these 8 differences will help you pick the right sensor for stable, efficient operation.
Learn More: Inductive vs Capacitive Sensor
Learn More: Inductive vs Hall Effect Sensor
Learn More: Inductive vs BLTouch