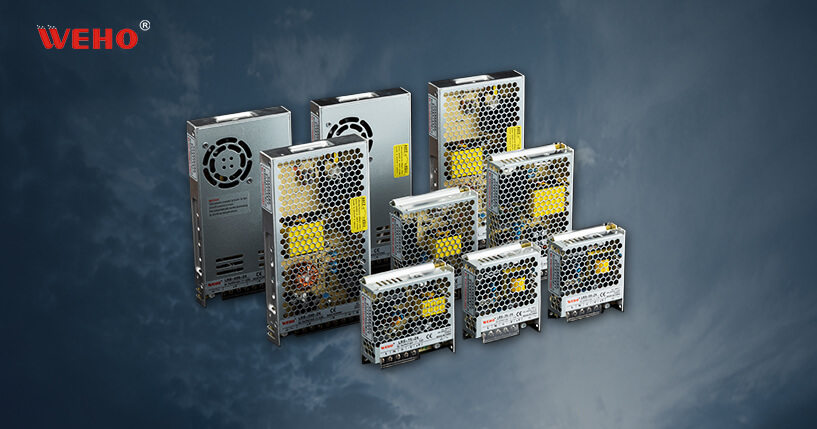
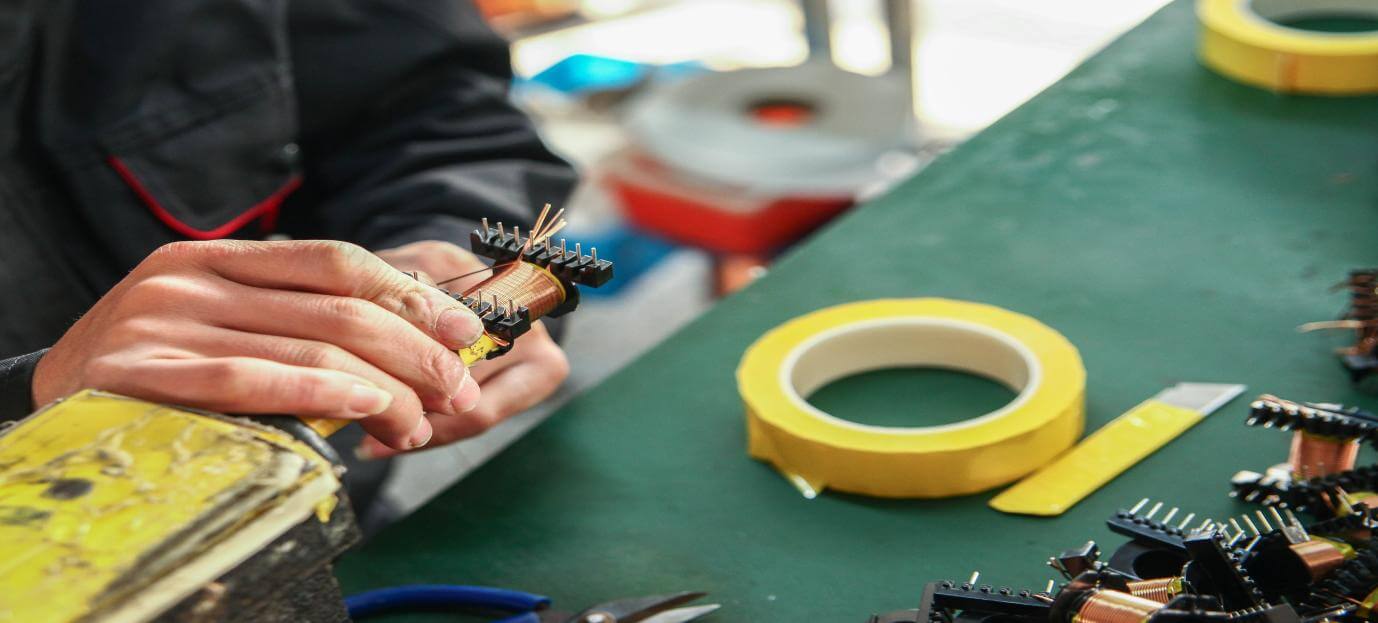
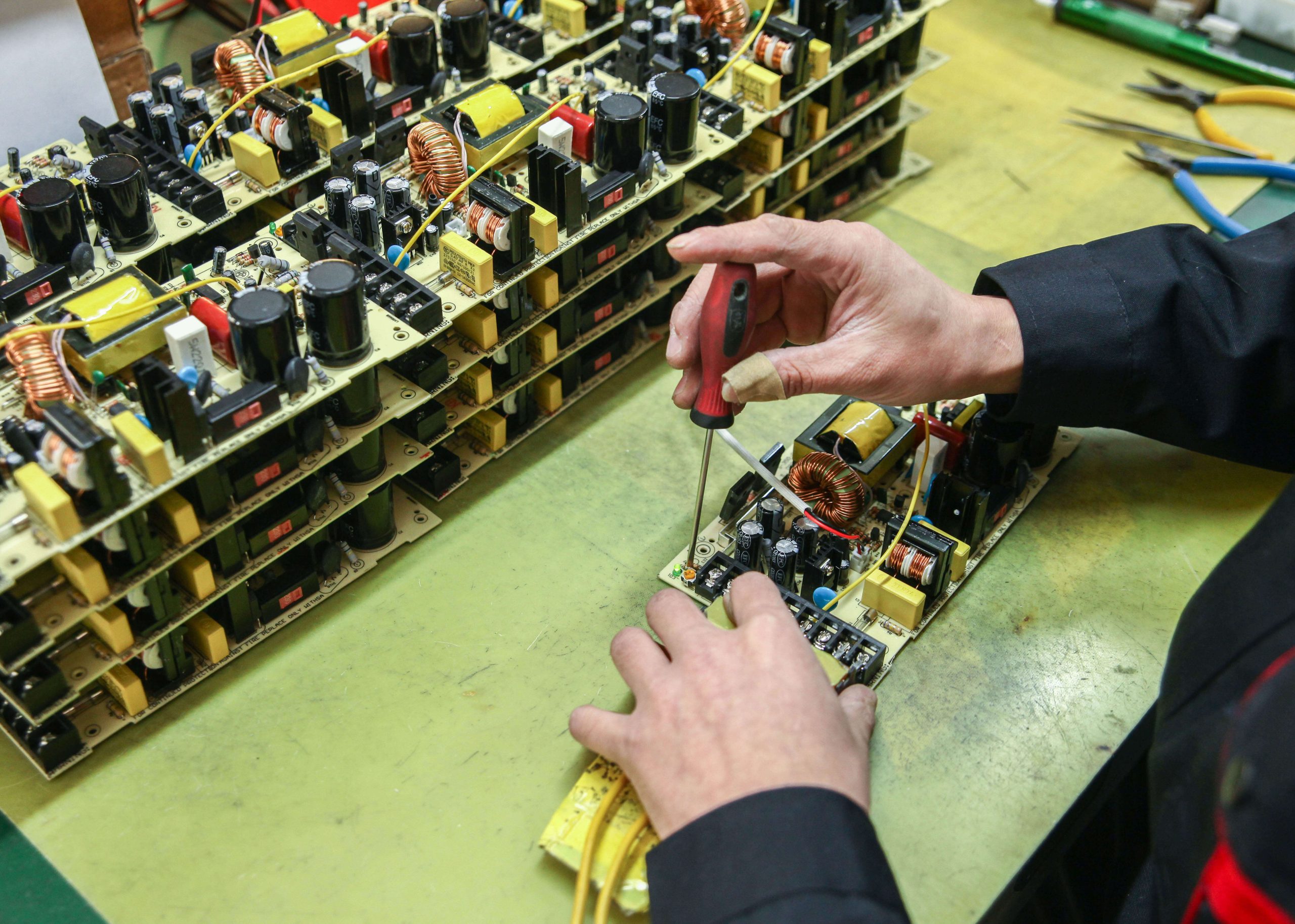
Components and functionality of a power supply
The main components of a power supply are transformers, rectifiers, and voltage regulators. The transformer is responsible for converting the voltage from the wall outlet to the voltage level required by the device. The rectifier converts the AC voltage output from the transformer into a DC voltage suitable for use by the equipment. The voltage regulator then provides a stable output voltage, ensuring that the device gets a stable power supply.
Power supplies may also include additional components such as fuses, capacitors, and inductors to help regulate and protect power and equipment. It is important to choose a power supply that is designed for your particular device and can deliver the necessary power and voltage levels.